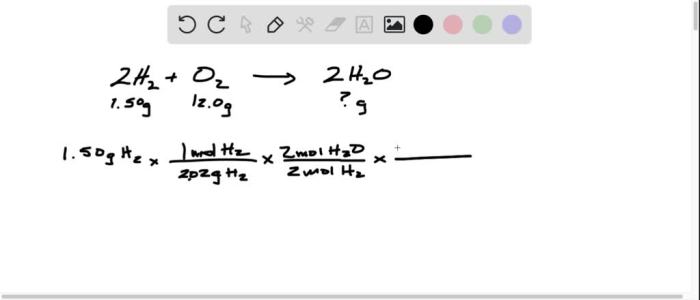
Embark on a captivating journey into the realm of acids and bases with Acids and Bases Worksheet #2. This comprehensive guide unravels the intricacies of these fundamental chemical concepts, offering a clear and engaging exploration of their properties, reactions, and applications.
Delve into the world of acids and bases, discovering their unique characteristics and the fascinating reactions that occur when they interact. Learn how to calculate pH and pOH, delve into the principles of acid-base titrations, and uncover the diverse industrial, environmental, and biological applications of these essential substances.
Understanding Acids and Bases: Acids And Bases Worksheet #2
Acids and bases are two important classes of chemical compounds that play a crucial role in various chemical reactions. Understanding their properties and behavior is essential for comprehending many chemical processes.Acids are substances that donate hydrogen ions (H+) in aqueous solutions.
They typically have a sour taste, react with metals to produce hydrogen gas, and turn blue litmus paper red. Common examples of acids include hydrochloric acid (HCl), sulfuric acid (H2SO4), and acetic acid (CH3COOH).Bases, on the other hand, are substances that accept hydrogen ions (H+) in aqueous solutions.
They usually have a bitter taste, feel slippery to the touch, and turn red litmus paper blue. Common examples of bases include sodium hydroxide (NaOH), potassium hydroxide (KOH), and ammonia (NH3).
Acid-Base Reactions
Acid-base reactions are chemical reactions that involve the transfer of protons (H+ ions) between reactants. These reactions are crucial in many biological and chemical processes.
There are three main types of acid-base reactions:
Neutralization Reactions
Neutralization reactions occur when an acid and a base react in stoichiometric proportions, resulting in the formation of a salt and water. For example, the reaction between hydrochloric acid (HCl) and sodium hydroxide (NaOH) produces sodium chloride (NaCl) and water (H2O):
HCl + NaOH → NaCl + H2O
Proton Transfer Reactions
Proton transfer reactions involve the transfer of a proton from an acid to a base. These reactions are often represented using the Brønsted-Lowry acid-base theory, which defines an acid as a proton donor and a base as a proton acceptor.
For example, the reaction between acetic acid (CH3COOH) and water produces hydronium ions (H3O+) and acetate ions (CH3COO-):
CH3COOH + H2O → H3O+ + CH3COO-
Hydrolysis Reactions
Hydrolysis reactions occur when a salt reacts with water, resulting in the formation of an acid and a base. For example, the hydrolysis of sodium acetate (CH3COONa) produces acetic acid (CH3COOH) and sodium hydroxide (NaOH):
CH3COONa + H2O → CH3COOH + NaOH
pH and pOH
pH and pOH are two important concepts in chemistry that are used to describe the acidity or basicity of a solution. pH is a measure of the concentration of hydrogen ions (H+) in a solution, while pOH is a measure of the concentration of hydroxide ions (OH-) in a solution.
The pH scale ranges from 0 to 14, with a pH of 7 being neutral. Solutions with a pH less than 7 are acidic, while solutions with a pH greater than 7 are basic. The pOH scale also ranges from 0 to 14, with a pOH of 7 being neutral.
Solutions with a pOH less than 7 are basic, while solutions with a pOH greater than 7 are acidic.
Calculating pH and pOH
The pH of a solution can be calculated using the following equation:
pH =
log[H+]
where [H+] is the molar concentration of hydrogen ions in the solution.
Acids and bases worksheet #2 is a great way to test your understanding of this topic. If you’re looking for some extra help, check out the pith ball lab gizmo answers . They can provide you with a step-by-step guide on how to solve the problems in the worksheet.
Once you’ve reviewed the answers, come back to acids and bases worksheet #2 and give it another try. You’ll be surprised at how much easier it is the second time around!
The pOH of a solution can be calculated using the following equation:
pOH =
log[OH-]
where [OH-] is the molar concentration of hydroxide ions in the solution.
Relationship between pH and pOH
The pH and pOH of a solution are related by the following equation:
pH + pOH = 14
This equation shows that the pH and pOH of a solution are always complementary. If the pH of a solution is high, the pOH of the solution will be low, and vice versa.
Acid-Base Titrations
Acid-base titrations are a crucial technique used in analytical chemistry to determine the concentration of an unknown acid or base solution. It involves the controlled addition of a known concentration of one solution (the titrant) to another solution (the analyte) until a specific reaction point is reached, known as the equivalence point.
Steps Involved in Acid-Base Titration, Acids and bases worksheet #2
An acid-base titration typically involves the following steps:
-
-*Preparation
Prepare the titrant and analyte solutions with known volumes and concentrations. Choose an appropriate indicator that changes color at or near the equivalence point.
-*Titration
Add the titrant solution from a burette to the analyte solution in a flask or beaker while constantly stirring. Record the volume of titrant added.
-*Endpoint
Observe the color change of the indicator, signaling the endpoint of the titration. The endpoint is close to but not necessarily identical to the equivalence point.
-*Calculation
Use the volume of titrant added and the stoichiometry of the reaction to calculate the concentration of the unknown acid or base solution.
Examples of Acid-Base Titrations
Acid-base titrations have various applications, including:
-
-*Standardizing Solutions
Determine the exact concentration of a known acid or base solution by titrating it against a primary standard.
-*Analyzing Acid or Base Content
Measure the concentration of an unknown acid or base solution in a sample.
-*Determining Equivalence Points
Find the exact point where the moles of acid and base are equal, which is useful in various chemical reactions and processes.
Applications of Acids and Bases
Acids and bases have a wide range of applications in various fields, including industry, environment, and biology. Their unique properties make them essential components in numerous processes.
Industrial Applications
In industries, acids and bases are used extensively in:
- Chemical Production:Acids are used to synthesize fertilizers, plastics, and other chemicals. Bases are used in the production of soaps, detergents, and paper.
- Metalworking:Acids are used to etch and clean metals. Bases are used to neutralize acidic waste from metalworking processes.
- Textile Manufacturing:Acids are used to dye and bleach fabrics. Bases are used to neutralize acidic dyes and to soften fabrics.
- Food Processing:Acids are used as preservatives and flavorings in food products. Bases are used to neutralize acidic foods and to tenderize meat.
Environmental Applications
In environmental protection, acids and bases play crucial roles in:
- Water Treatment:Acids are used to neutralize alkaline water. Bases are used to neutralize acidic water.
- Wastewater Treatment:Acids are used to coagulate pollutants in wastewater. Bases are used to neutralize acidic wastewater.
- Soil Remediation:Acids are used to neutralize alkaline soils. Bases are used to neutralize acidic soils.
- Air Pollution Control:Acids are used to remove ammonia from industrial emissions. Bases are used to remove sulfur dioxide from industrial emissions.
Biological Applications
In biological systems, acids and bases are essential for:
- pH Regulation:Acids and bases help maintain the pH balance in cells and body fluids, which is crucial for proper functioning.
- Digestion:Acids in the stomach help break down food. Bases in the intestines help neutralize acidic stomach contents.
- Metabolism:Acids and bases are involved in various metabolic processes, including energy production and waste elimination.
- Enzyme Activity:Acids and bases can affect the activity of enzymes, which are essential for biological reactions.
General Inquiries
What is the difference between an acid and a base?
Acids release hydrogen ions (H+) in water, while bases release hydroxide ions (OH-) in water.
What is the pH scale?
The pH scale measures the acidity or basicity of a solution, ranging from 0 (highly acidic) to 14 (highly basic).
What is the purpose of an acid-base titration?
Acid-base titrations are used to determine the concentration of an unknown acid or base by reacting it with a known concentration of the other.