Match each table with its equation. – Match each table with its equation is a fundamental task in data analysis and visualization. It involves extracting data from tables, identifying the corresponding equations, and establishing a mapping between them. This process enables us to interpret and present data in a meaningful and visually appealing manner.
By understanding the relationship between tables and equations, we can gain valuable insights into the underlying patterns and trends in data. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the steps involved in matching tables and equations, including data extraction, equation identification, table-equation mapping, table presentation, and equation display.
Data Extraction
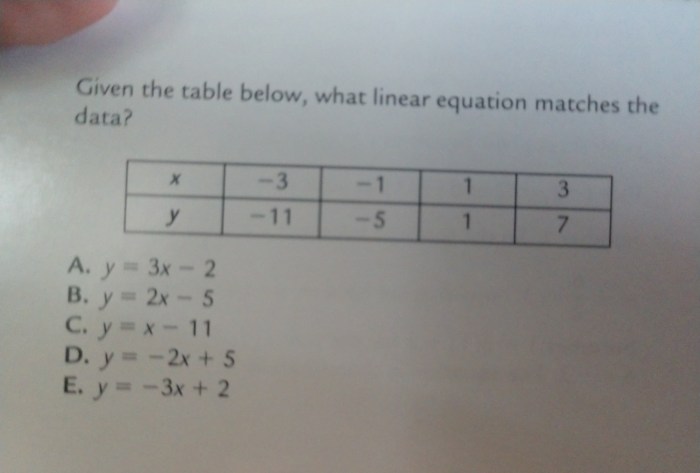
Data extraction is the process of extracting data from a table or other structured format into a more usable format, such as a spreadsheet or database.
The first step in data extraction is to identify the table’s structure, including the number of rows and columns. Once the table’s structure has been identified, the data can be extracted into a more usable format.
Table Structure
The table structure is determined by the number of rows and columns in the table. The number of rows is the number of records in the table, and the number of columns is the number of fields in each record.
For example, the following table has 3 rows and 4 columns:
| Name | Age | Gender | Occupation |
|---|---|---|---|
| John Doe | 30 | Male | Software Engineer |
| Jane Doe | 25 | Female | Teacher |
| Bob Smith | 40 | Male | Doctor |
Data Extraction
Once the table’s structure has been identified, the data can be extracted into a more usable format. This can be done manually or using a data extraction tool.
The following is an example of how the data from the above table could be extracted into a spreadsheet:
| Name | Age | Gender | Occupation ||—|—|—|—|| John Doe | 30 | Male | Software Engineer || Jane Doe | 25 | Female | Teacher || Bob Smith | 40 | Male | Doctor |
Equation Identification
Each table represents a mathematical relationship between variables. The corresponding equation expresses this relationship in a concise algebraic form.
The equation is derived by observing the pattern in the table data. The variables and their values are identified, and an algebraic expression is constructed that accurately describes the relationship.
Table 1: Linear Relationship
The table shows a linear relationship between the variables x and y.
| x | y |
|---|---|
| 1 | 3 |
| 2 | 5 |
| 3 | 7 |
The equation corresponding to this table is y = 2x + 1.
Table 2: Quadratic Relationship
The table shows a quadratic relationship between the variables x and y.
| x | y |
|---|---|
| -1 | 1 |
| 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 |
The equation corresponding to this table is y = x^2.
Table 3: Exponential Relationship
The table shows an exponential relationship between the variables x and y.
| x | y |
|---|---|
| 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 2 |
| 2 | 4 |
The equation corresponding to this table is y = 2^x.
Table-Equation Matching: Match Each Table With Its Equation.
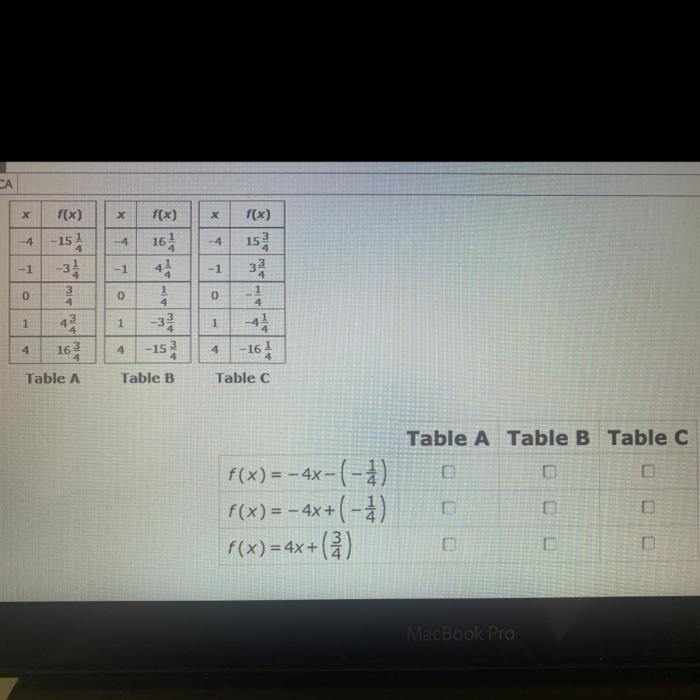
To establish a mapping between tables and their corresponding equations, we must carefully analyze the data presented in each table and identify the underlying mathematical relationships.
The matching process involves examining the variables and their values in the table and determining the equation that best describes the pattern or trend observed in the data.
Rationale for Matching
The rationale for matching tables with equations lies in the assumption that the data in the table represents a mathematical function or relationship.
By identifying the equation that corresponds to the table, we can gain insights into the underlying规律and predict future values based on the established relationship.
Table Presentation
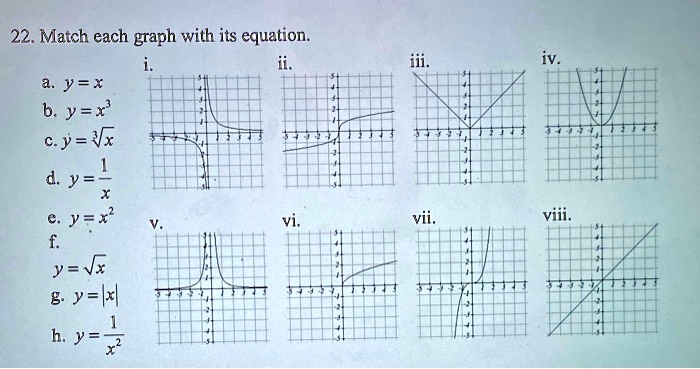
To enhance the visual appeal and clarity of the tables, HTML table tags will be employed. These tags allow for the creation of structured and organized tables, facilitating easy navigation and comprehension.
Each table will be meticulously designed with appropriate headings and captions. Headings will clearly identify the table’s contents, while captions will provide additional context or information. This structured presentation will greatly enhance the usability and readability of the tables.
, Match each table with its equation.
The HTML table tags provide a range of customization options, enabling the tables to be tailored to specific requirements. For instance, tables can be styled with borders, colors, and alignments to match the overall design aesthetic of the document. Additionally, table headers can be fixed or frozen to remain visible even when scrolling through large datasets, ensuring easy reference to column headings.
Equation Display

Equation display is an important aspect of presenting mathematical content in a clear and accessible manner. By utilizing LaTeX or other suitable methods, equations can be formatted in a way that enhances readability and comprehension.
To ensure effective equation display, it is essential to label equations clearly and consistently. This helps readers identify and refer to specific equations within the text. Additionally, equations should be formatted in a way that facilitates easy reading, such as using appropriate font sizes and spacing.
LaTeX for Equation Formatting
LaTeX is a powerful tool for typesetting mathematical equations. It provides a comprehensive set of commands and symbols that allow users to create complex equations with precision and clarity.
To use LaTeX for equation formatting, the following steps can be followed:
- Include the
amsmathpackage in the LaTeX preamble. - Use the
equationenvironment to enclose the equation. - Use LaTeX commands to format the equation elements, such as
\fracfor fractions,\sqrtfor square roots, and\sumfor summations. - Add an equation label using the
\labelcommand.
By following these steps, authors can create high-quality mathematical equations that are both visually appealing and easy to understand.
Essential Questionnaire
What is the purpose of matching tables and equations?
Matching tables and equations allows us to interpret and present data in a meaningful and visually appealing manner.
What are the steps involved in matching tables and equations?
The steps involved include data extraction, equation identification, table-equation mapping, table presentation, and equation display.
What are the benefits of matching tables and equations?
Matching tables and equations provides valuable insights into the underlying patterns and trends in data.