Vitamin D deficiency crossword clue: a cryptic hint that leads us down a path to uncover the causes, symptoms, and treatment of this prevalent health concern. This essential nutrient plays a crucial role in maintaining overall well-being, and its deficiency can have far-reaching implications.
From the sun’s warm embrace to dietary sources and the potential risks associated with its absence, this comprehensive exploration delves into the complexities of vitamin D deficiency, unraveling its impact on our physical and physiological health.
Vitamin D Deficiency
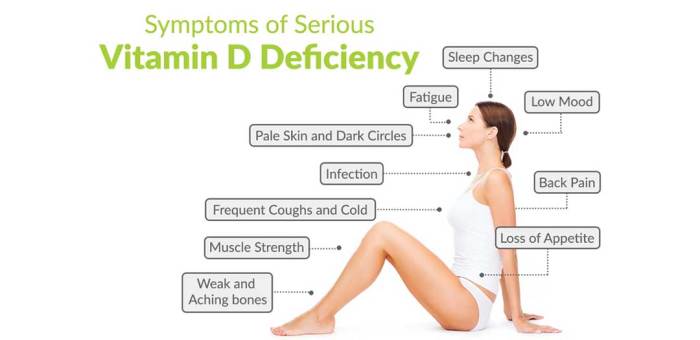
Vitamin D deficiency is a condition in which the body does not have enough vitamin D. Vitamin D is a nutrient that is essential for bone health and overall well-being. It is produced by the body when exposed to sunlight, and it can also be obtained from certain foods and supplements.There
are many causes of vitamin D deficiency, including:
- Lack of exposure to sunlight
- Dark skin pigmentation
- Certain medical conditions, such as kidney disease and liver disease
- Certain medications, such as corticosteroids and anticonvulsants
- Malabsorption disorders, such as celiac disease and Crohn’s disease
Vitamin D deficiency can lead to a number of health problems, including:
- Osteoporosis, a condition that causes bones to become weak and brittle
- Osteomalacia, a condition that causes bones to become soft and flexible
- Muscle weakness
- Fatigue
- Depression
Vitamin D is essential for overall health. It is important to get enough vitamin D from sunlight, food, or supplements to prevent deficiency and its associated health problems.
Importance of Vitamin D, Vitamin d deficiency crossword clue
Vitamin D is essential for a number of important bodily functions, including:
- Bone health: Vitamin D helps the body absorb calcium, which is essential for strong bones.
- Muscle function: Vitamin D helps the body absorb calcium, which is also essential for muscle function.
- Immune function: Vitamin D helps the body fight off infection.
- Mood regulation: Vitamin D has been linked to improved mood and reduced risk of depression.
Getting enough vitamin D is important for overall health and well-being.
Vitamin D Sources

Vitamin D is an essential nutrient that plays a crucial role in maintaining bone health, muscle function, and immune system regulation. It is primarily obtained through three main sources: food, sunlight exposure, and supplements.
Food Sources
- Fatty fish:Salmon, tuna, mackerel, and sardines are excellent sources of vitamin D, providing up to 1,000 IU per serving.
- Eggs:Egg yolks contain a significant amount of vitamin D, with one large egg providing approximately 40 IU.
- Dairy products:Milk, yogurt, and cheese are fortified with vitamin D, typically providing 100-150 IU per serving.
- Mushrooms:Certain types of mushrooms, such as shiitake and oyster mushrooms, contain vitamin D when exposed to sunlight during growth.
Sunlight Exposure
The human body can synthesize vitamin D when exposed to sunlight. The ultraviolet B (UVB) rays in sunlight trigger a chemical reaction in the skin that produces vitamin D3. The amount of vitamin D produced depends on factors such as the intensity of sunlight, duration of exposure, and skin pigmentation.
Supplements
For individuals who do not get enough vitamin D from food or sunlight, supplements can be an effective way to prevent deficiency. Vitamin D supplements are available in various forms, including capsules, tablets, and liquid drops. The recommended daily intake of vitamin D varies depending on age, health status, and sun exposure.
Health Implications: Vitamin D Deficiency Crossword Clue
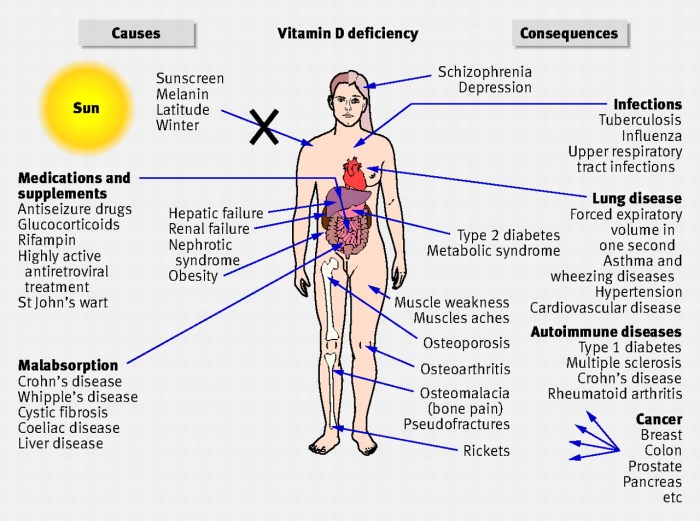
Vitamin D deficiency can have severe health implications, affecting various bodily functions.
One of the most significant consequences of vitamin D deficiency is osteoporosis, a condition characterized by weak and brittle bones. Vitamin D plays a crucial role in calcium absorption, which is essential for bone mineralization. Insufficient vitamin D levels can impair calcium absorption, leading to decreased bone density and an increased risk of fractures.
Immune Function
Vitamin D also plays a vital role in immune function. It helps regulate the production and activity of immune cells, including T cells and macrophages. Deficiency in vitamin D can impair immune responses, making individuals more susceptible to infections and autoimmune diseases.
Diagnosis and Treatment

Vitamin D deficiency is diagnosed based on blood tests that measure serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D [25(OH)D] levels. The reference ranges for vitamin D levels vary depending on the laboratory, but generally:
Interpreting Vitamin D Blood Test Results
- Deficient:Less than 20 ng/mL (50 nmol/L)
- Insufficient:20-29 ng/mL (50-72 nmol/L)
- Sufficient:30-100 ng/mL (75-250 nmol/L)
- Toxic:Greater than 150 ng/mL (375 nmol/L)
Treatment for vitamin D deficiency typically involves oral supplementation with vitamin D2 (ergocalciferol) or vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol). The recommended daily intake for adults is 600-800 IU, but higher doses may be necessary in certain cases.
Treatment Options for Vitamin D Deficiency
- Oral supplements:Vitamin D2 or vitamin D3 can be taken orally in capsule or tablet form.
- Injections:In severe cases, vitamin D can be administered intramuscularly or intravenously.
- Diet:Foods rich in vitamin D, such as fatty fish, eggs, and fortified milk, can contribute to vitamin D intake.
- Sunlight exposure:Exposure to sunlight triggers the production of vitamin D in the skin, but it is important to practice sun safety measures.
It is important to note that vitamin D supplementation should be monitored by a healthcare professional to avoid potential toxicity.
Q&A
What are the primary causes of vitamin D deficiency?
Insufficient sun exposure, limited dietary intake, and certain medical conditions can contribute to vitamin D deficiency.
What are some common symptoms associated with vitamin D deficiency?
Bone pain, muscle weakness, fatigue, and an increased susceptibility to infections are potential symptoms.
Why is vitamin D important for overall health?
Vitamin D plays a vital role in calcium absorption, bone health, immune function, and overall well-being.