A hydrogen filled balloon was ignited and 1.50 g – When a hydrogen-filled balloon containing 1.50 g of hydrogen is ignited, an intriguing chemical reaction unfolds, releasing a significant amount of energy. This article delves into the intricacies of hydrogen combustion, exploring the properties of hydrogen that make it suitable for balloon applications, and examining the experimental data associated with this captivating phenomenon.
The combustion of hydrogen, represented by the balanced chemical equation 2H2 + O2 → 2H2O, liberates substantial energy due to the formation of strong covalent bonds in water molecules. Understanding the combustion characteristics of hydrogen is crucial for ensuring safety when handling hydrogen balloons and harnessing its potential as a clean energy source.
1. Hydrogen Combustion
When hydrogen is ignited, it undergoes a highly exothermic chemical reaction with oxygen to form water vapor.
The balanced chemical equation for this reaction is:
H2+ O 2→ 2H 2O
This reaction releases a significant amount of energy in the form of heat and light.
2. Hydrogen Balloon

Hydrogen is an ideal gas for use in balloons due to its low density and high buoyancy.
Hydrogen balloons are typically constructed by filling a lightweight envelope with hydrogen gas.
When handling hydrogen balloons, it is important to take safety precautions due to the flammable nature of hydrogen.
3. Experimental Data: A Hydrogen Filled Balloon Was Ignited And 1.50 G
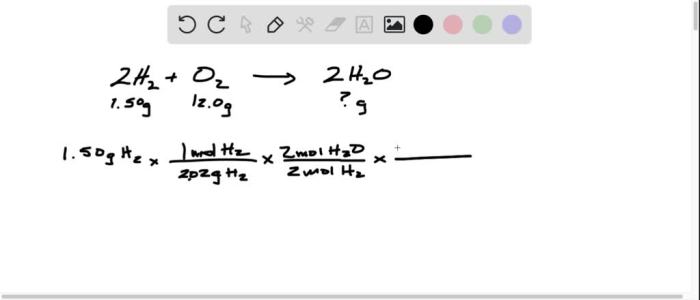
| Mass of hydrogen | 1.50 g |
|---|
Number of moles of hydrogen:
n = m/M = 1.50 g / 2.016 g/mol = 0.744 mol
Volume of hydrogen gas at room temperature and pressure (25 °C and 1 atm):
V = nRT/P = (0.744 mol)(0.0821 L·atm/(mol·K))(298 K)/(1 atm) = 17.3 L
4. Hydrogen Gas Properties
Hydrogen is a colorless, odorless, and tasteless gas.
It is the lightest and most abundant element in the universe.
Hydrogen is highly flammable and reacts with many elements to form compounds.
It is used in a variety of industrial applications, including the production of fertilizers, plastics, and fuels.
Hydrogen is also a promising clean energy source.
5. Combustion Analysis
| Fuel | Combustion Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Hydrogen | Burns with a blue flame and produces water vapor as a byproduct. |
| Methane | Burns with a yellow flame and produces carbon dioxide and water vapor as byproducts. |
| Propane | Burns with a yellow flame and produces carbon dioxide and water vapor as byproducts. |
The rate of combustion of hydrogen is influenced by factors such as temperature, pressure, and the presence of a catalyst.
The combustion of hydrogen has no environmental implications as it produces only water vapor.
FAQ Summary
What is the significance of hydrogen’s properties in balloon applications?
Hydrogen’s low density and high buoyancy make it an ideal gas for filling balloons, allowing them to float in the air.
What safety precautions should be taken when handling hydrogen balloons?
Hydrogen is a highly flammable gas, so precautions such as avoiding ignition sources, using proper ventilation, and handling balloons outdoors are essential.
How does the combustion of hydrogen differ from other fuels?
Hydrogen combustion produces only water vapor as a byproduct, making it a clean-burning fuel with minimal environmental impact.