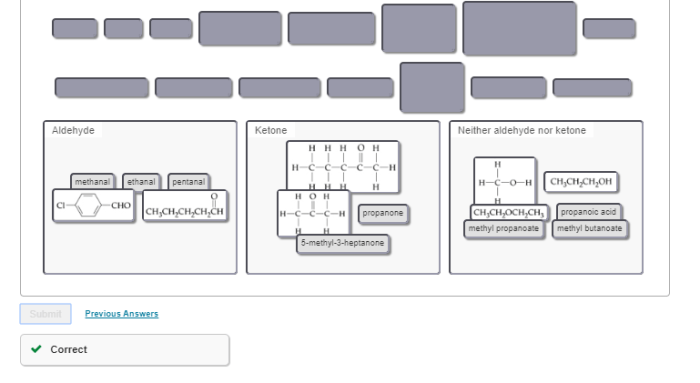
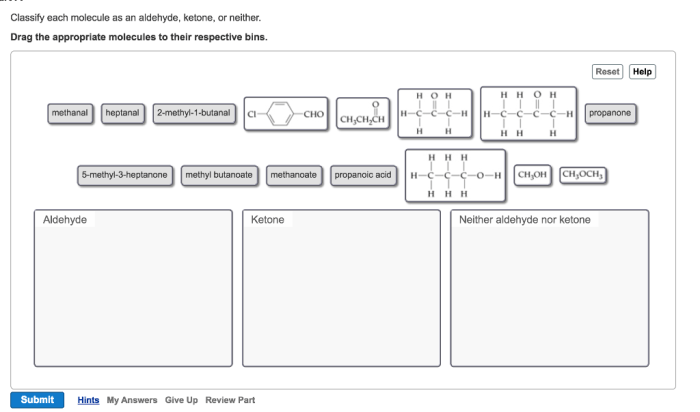
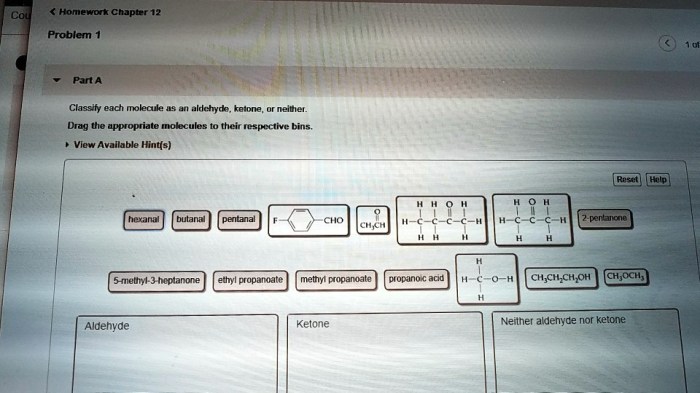
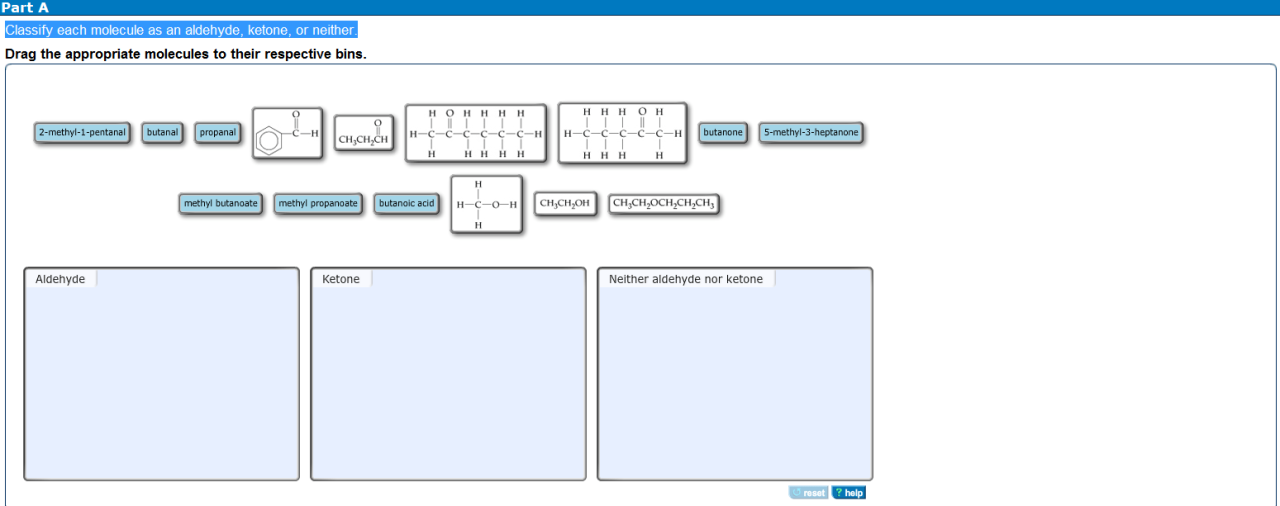
Classify each molecule as an aldehyde ketone or neither – Delving into the fascinating realm of organic chemistry, we embark on a journey to classify molecules as aldehydes, ketones, or neither. Aldehydes and ketones, both carbonyl compounds, play crucial roles in various biological processes and industrial applications. Understanding their distinct characteristics and functional groups is paramount in comprehending their diverse reactivity and significance.
Throughout this exploration, we will delve into the structural intricacies of aldehydes and ketones, unraveling their unique chemical properties. We will also examine molecules that defy these classifications, expanding our understanding of organic compound diversity. Join us as we unravel the captivating world of carbonyl chemistry, unlocking the secrets of molecular classification.
Aldehydes: Classify Each Molecule As An Aldehyde Ketone Or Neither
Aldehydes are organic compounds that contain a carbonyl group (C=O) and at least one hydrogen atom attached to the carbon atom of the carbonyl group. They are characterized by the functional group -CHO.
Chemical Structure of Aldehydes
The general chemical structure of aldehydes is R-CHO, where R represents an alkyl, aryl, or hydrogen group.
Functional Group of Aldehydes
The functional group of aldehydes is the carbonyl group (C=O). The carbon atom in the carbonyl group is sp 2hybridized and forms a double bond with the oxygen atom.
Examples of Aldehydes
- Formaldehyde (HCHO)
- Acetaldehyde (CH 3CHO)
- Benzaldehyde (C 6H 5CHO)
Naming Convention for Aldehydes
Aldehydes are named by adding the suffix “-al” to the parent hydrocarbon name. For example, the aldehyde derived from methane is called methanal.
Ketones
Ketones are organic compounds that contain a carbonyl group (C=O) and two alkyl or aryl groups attached to the carbon atom of the carbonyl group. They are characterized by the functional group -CO-.
Chemical Structure of Ketones
The general chemical structure of ketones is R 1-CO-R 2, where R 1and R 2represent alkyl, aryl, or hydrogen groups.
Functional Group of Ketones
The functional group of ketones is the carbonyl group (C=O). The carbon atom in the carbonyl group is sp 2hybridized and forms a double bond with the oxygen atom.
Examples of Ketones
- Acetone (CH 3COCH 3)
- 2-Butanone (CH 3CH 2COCH 3)
- Benzophenone (C 6H 5COC 6H 5)
Naming Convention for Ketones, Classify each molecule as an aldehyde ketone or neither
Ketones are named by adding the suffix “-one” to the parent hydrocarbon name. For example, the ketone derived from propane is called propanone.
Neither Aldehydes nor Ketones
Compounds that are neither aldehydes nor ketones do not contain a carbonyl group (C=O). They may contain other functional groups, such as alcohols (-OH), ethers (-O-), or carboxylic acids (-COOH).
Examples of Compounds that are Neither Aldehydes nor Ketones
- Alcohols: Ethanol (CH 3CH 2OH)
- Ethers: Diethyl ether (CH 3CH 2OCH 2CH 3)
- Carboxylic acids: Acetic acid (CH 3COOH)
Chemical Structures of Compounds that are Neither Aldehydes nor Ketones
The chemical structures of compounds that are neither aldehydes nor ketones vary depending on the functional group present. For example, alcohols have a hydroxyl group (-OH), ethers have an ether group (-O-), and carboxylic acids have a carboxyl group (-COOH).
Functional Groups of Compounds that are Neither Aldehydes nor Ketones
The functional groups of compounds that are neither aldehydes nor ketones determine their chemical properties and reactivity. For example, alcohols can undergo oxidation to form aldehydes or ketones, ethers are relatively inert, and carboxylic acids can undergo a variety of reactions, including neutralization, esterification, and decarboxylation.
Classification of Molecules
| Molecule | Structure | Functional Group | Classification |
|---|---|---|---|
| Formaldehyde | HCHO | -CHO | Aldehyde |
| Acetone | CH3COCH3 | -CO- | Ketone |
| Ethanol | CH3CH2OH | -OH | Neither |
| Diethyl ether | CH3CH2OCH2CH3 | -O- | Neither |
General Inquiries
What is the key difference between aldehydes and ketones?
Aldehydes possess a hydrogen atom bonded to the carbonyl carbon, while ketones have two alkyl or aryl groups attached to the carbonyl carbon.
Can a molecule contain both aldehyde and ketone functional groups?
No, a molecule cannot simultaneously possess both aldehyde and ketone functional groups.
What is an example of a compound that is neither an aldehyde nor a ketone?
Esters, such as ethyl acetate, lack the carbonyl group characteristic of aldehydes and ketones.