Match each fatty acid with its melting point to unveil the intricate relationship between fatty acid structure and its physical properties. Delve into the fascinating world of lipids as we explore the factors that influence melting points and uncover the practical applications of this knowledge in diverse fields.
This comprehensive guide provides a deep dive into the types of fatty acids, examining their chemical formulas and melting points. We will explore the impact of chain length, unsaturation, and branching on melting behavior, utilizing real-world examples to illustrate these concepts.
1. Introduction

Understanding fatty acid melting points is crucial for various fields, including food science, nutrition, and medicine. Melting point is a key indicator of a fatty acid’s physical properties and its behavior in different environments.
The melting point of a fatty acid is directly related to its structure. Saturated fatty acids, which have only single bonds between their carbon atoms, have higher melting points than unsaturated fatty acids, which have one or more double bonds between their carbon atoms.
2. Types of Fatty Acids
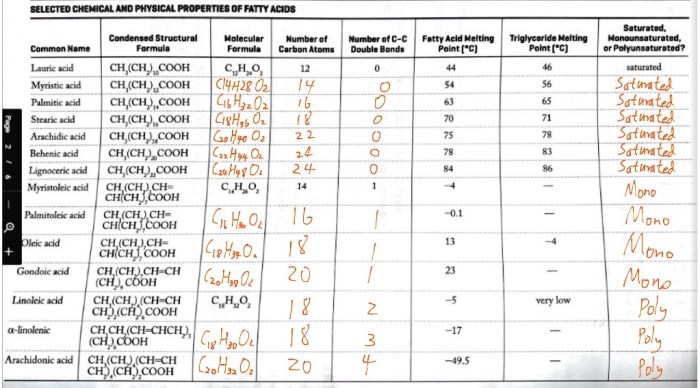
| Fatty Acid Name | Chemical Formula | Melting Point (°C) |
|---|---|---|
| Butyric acid | CH3(CH2)2COOH | -7.9 |
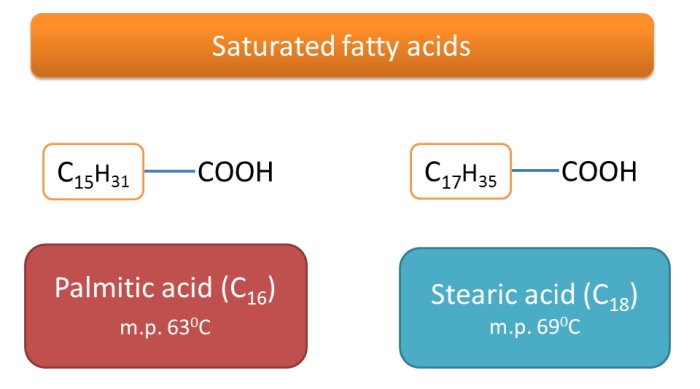
| Palmitic acid | CH3(CH2)14COOH | 62.9 |
| Oleic acid | CH3(CH2)7CH=CH(CH2)7COOH | 13.4 |
| Linoleic acid | CH3(CH2)4CH=CHCH2CH=CH(CH2)7COOH | -5.3 |
| α-Linolenic acid | CH3CH2CH=CHCH2CH=CHCH2CH=CH(CH2)7COOH | -11.1 |
3. Factors Affecting Melting Point
Chain Length
As the chain length of a fatty acid increases, its melting point generally increases. This is because longer chains have stronger van der Waals forces between their molecules.
Degree of Unsaturation, Match each fatty acid with its melting point
Unsaturated fatty acids have lower melting points than saturated fatty acids. This is because the double bonds in unsaturated fatty acids create kinks in the chain, which prevents the molecules from packing together as tightly.
Branching
Branching in a fatty acid chain can lower the melting point. This is because the branching creates irregularities in the chain, which makes it more difficult for the molecules to pack together.
4. Applications of Melting Point Data
Food Science
Melting point data is used in food science to predict the behavior of fats and oils in different food products. For example, the melting point of a fat can affect the texture of a baked good or the spreadability of a margarine.
Nutrition
Melting point data is used in nutrition to understand the health effects of different types of fats. For example, saturated fats have higher melting points than unsaturated fats, and they are associated with an increased risk of heart disease.
Medicine
Melting point data is used in medicine to develop drugs and treatments for a variety of diseases. For example, the melting point of a drug can affect its solubility and bioavailability.
5. Melting Point Determination
Capillary Tube Method
The capillary tube method is a simple and inexpensive way to determine the melting point of a fatty acid. A small sample of the fatty acid is placed in a capillary tube and heated gradually. The melting point is the temperature at which the fatty acid melts and flows out of the capillary tube.
Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
DSC is a more precise method for determining the melting point of a fatty acid. A sample of the fatty acid is placed in a DSC cell and heated gradually. The DSC measures the heat flow into or out of the sample as it undergoes phase transitions, such as melting.
The melting point is the temperature at which the heat flow into the sample is greatest.
FAQ Compilation: Match Each Fatty Acid With Its Melting Point
What factors affect the melting point of a fatty acid?
Chain length, degree of unsaturation, and the presence of branching all influence the melting point of a fatty acid.
How is the melting point of a fatty acid determined?
Various methods can be used to determine the melting point of a fatty acid, including capillary tube methods and differential scanning calorimetry.
What are the applications of melting point data in food science?
Melting point data is used in food science to optimize the texture and stability of food products, such as margarine and chocolate.